Sorting Algorithms : Selection Sort
选择排序的定义(Selection Sort Definition)
Wikipedia 上对选择排序(Selection Sort)描述:
是一种简单直观的排序算法,是一种原地(in-place)的比较排序。
首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置
再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾
以此类推,直到所有元素均排序完毕。
它具有 O(n^2) 时间复杂度,所以在有着大量数据的序列中执行效率低下,并且通常比与它相似的插入排序(Insertion Sort)执行效率更低。
但选择排序以其简单性著称,在某些情况下,特别是在计算机存储器(Computer Data Storage)数量有限的情况下,它比其他更复杂的算法具有性能优势。
算法示例(Example)
从右到左循环遍历 n - 1 次列表,第一次循环遍历列表时,从列表中找出未排序子列表中的
最大值(maximum)的下标值pos,然后通过交换下标值为pos元素和下标值为n -1元素(即把最大值存放到列表中的已排序子列表中),然后列表长度n进行减 1操作。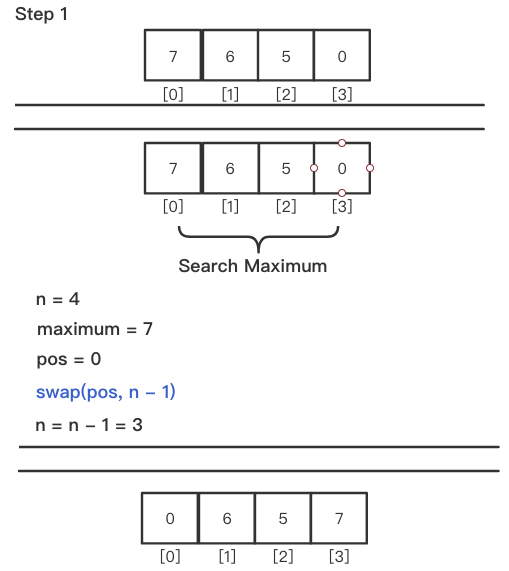
对于剩余的循环,将执行
步骤 1相同的过程。直至到循环遍历完第n - 1次时,列表排序完成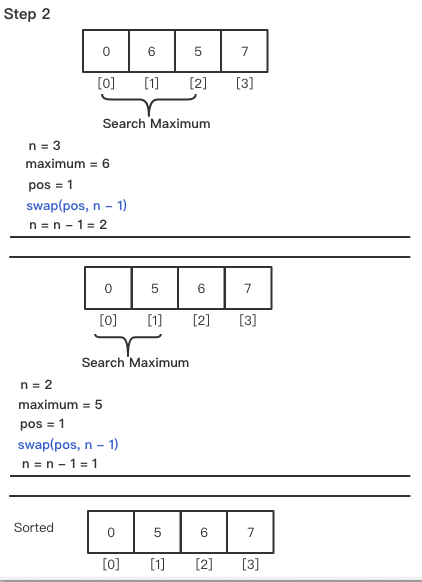
算法复杂度(Algorithm Complexity)
| Pass | Number of Comparisons |
|---|---|
1st |
(n - 1) |
2nd |
(n - 2) |
3rd |
(n - 3) |
... |
... |
last |
1 |
总的比较次数:(n - 1) + (n - 2) +(n - 3) + ... + 1 = n(n - 1) / 2 接近等于 n^2,因此复杂度为 O(n^2)
同时我们可以通过简单地观察循环次数来分析复杂性,因为算法使用了 2 个循环,因此复杂度为 O(n * n ) =O(n^2)
时间复杂度(Time Complexities):
最坏情况的复杂度:
O(n^2)如果我们想按升序排序数组,但数组已经是按照降序排列好的,那么最坏的情况就会发生。
最好情况的复杂度:
O(n^2)如果数组已经是排序完成。
平均情况的复杂度:
O(n^2)当数组的元素是混乱的顺序(既不是升序也不是降序)时,就会发生这种情况。
选择排序的时间复杂度在所有情况下都是相同的。在每一步,都必须找到最小元素(最大元素)并将其放在正确的位置。在未到循环结束之前,都不能确定最小元素(最大元素)。
空间复杂度(Space Complexity):
- 因为需要一个临时变量 temp 用于交换,因此空间复杂度为
O(1)
稳定性(Stability):
稳定性概念
如果 a 原本在 b 前面,而 a = b,排序之后 a 仍然在 b 的前面,那么说明该排序是稳定的,反之说明该排序是不稳定的。选择排序是不稳定的(Unstable)
选择排序的应用(Selection Sort Applications)
选择排序使用于以下的情况:
小量数据的列表。
不需考虑交换元素的成本
强制性需要检查所有的元素
写入存储器的成本与闪存相同(与冒泡排序的
O(n2)相比,选择排序的写入/交换次数为O(n))
代码实现(Code and Implementation)
C 语言实现
// C program for implementation of selection sort
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int arr[], int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Find the maximum element position in unsorted array
int findMaximumPos(int arr[], int n) {
int max = arr[0];
int pos = 0;
int i;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
pos = i;
}
}
return pos;
}
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n) {
// 从右到左循环遍历 n - 1 次数组
while (n > 1) {
int pos = findMaximumPos(arr, n);
swap(arr, pos, n - 1);
n--;
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main() {
int arr[] = {7, 6, 5, 0};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Array before sorting: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
selectionSort(arr, n);
printf("\nArray after sorting: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
参考(References)
Programiz - Selection Sort Algorithm : https://www.programiz.com/dsa/selection-sort
GeeksforGeeks - Selection Sort : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/selection-sort/
B 站 UP 主 - 正月点灯笼 - [算法教程] 几种经典排序的实现 : https://www.bilibili.com/video/av9830014
Wikipedia - Selection sort : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selection_sort
